Weather
ASIA, BERKELEY EARTH, BERKELEY EARTH TEAM, BRITISH, CALIFORNIA, CLIMATE, COPERNICUS, COPERNICUS CLIMATE SERVICE, EARTH, EUROPE, EUROPEAN COMMISSION, EXTREME WEATHER, GAVIN SCHMIDT, GLOBAL WARMING, GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS, JAPAN, METEOR, NASA, NATIONAL OCEANIC AND ATMOSPHERIC ADMINISTRATION, NO, NORTH AMERICA, SAMANTHA BURGESS, U. S, UNITED KINGDOM, UNITED KINGDOM ' S METEOROLOGY OFFICE, UNITED STATES, WEATHER, WEATHER AGENCY, WILDFIRES, WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION
Ethan Kim
0 Comments
Earth Hits Record Heat and Crosses Critical Climate Threshold in 2024
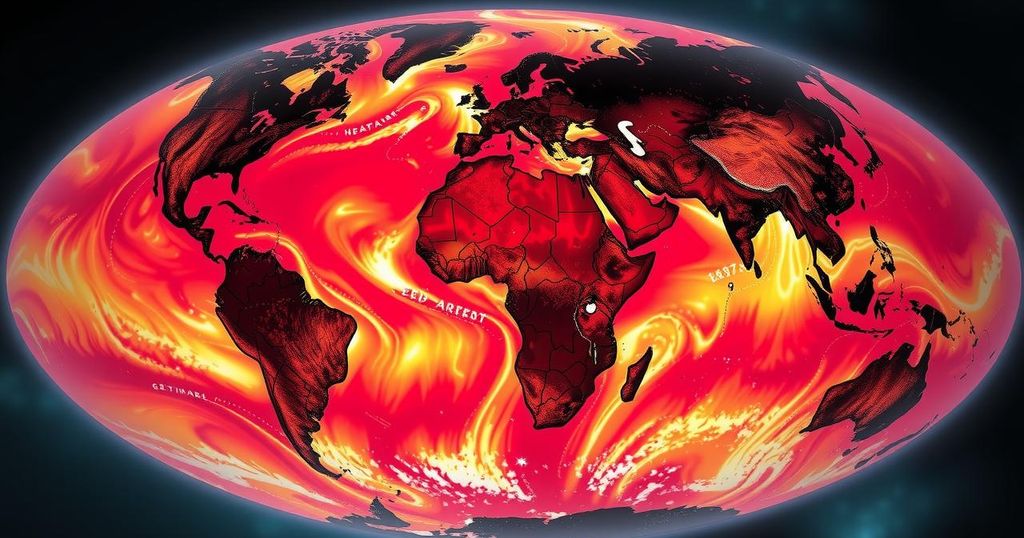
The Earth experienced its hottest year on record in 2024, surpassing the critical 1.5 degrees Celsius warming threshold for the entire year. This alarming trend has led to numerous climate-related disasters, with significant economic damages, posing severe risks to human life and ecosystems, underscoring the immediate need for effective climate action.
For the first time in recorded history, Earth registered an average temperature that exceeded the critical threshold of 1.5 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels for a full year, according to multiple weather monitoring agencies. The year 2024 not only marked the hottest year on record, but it also amplified the ongoing climate crisis, resulting in severe weather events globally, including 27 disasters within the United States that each inflicted over a billion dollars in damages. These alarming statistics highlight the significant and potentially irreversible impacts of climate change, emphasizing the drastic measures needed to mitigate further warming and related catastrophes.
The global average temperature increase is a direct consequence of the relentless accumulation of greenhouse gases, primarily due to human activities like fossil fuel combustion. The Paris Agreement aimed to limit the rise in temperature to 1.5 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels as a vital target for preserving ecological balance and preventing catastrophic climate impacts. However, the recent rise beyond this threshold signifies a critical breach, prompting urgent calls for action to curb greenhouse gas emissions.
The surpassing of the 1.5 degrees Celsius threshold underscores both the severity of the climate crisis and the urgent need for global cooperation to mitigate warming. The increased frequency of extreme weather events and the associated financial toll further highlight the dire consequences of inaction. Continuing on this trajectory may lead to irreparable damage to ecosystems and vast human suffering, compelling stakeholders to prioritize climate action effectively.
Original Source: www.keranews.org



Post Comment