Active Yet Uneven: The 2024 Atlantic Hurricane Season Summary
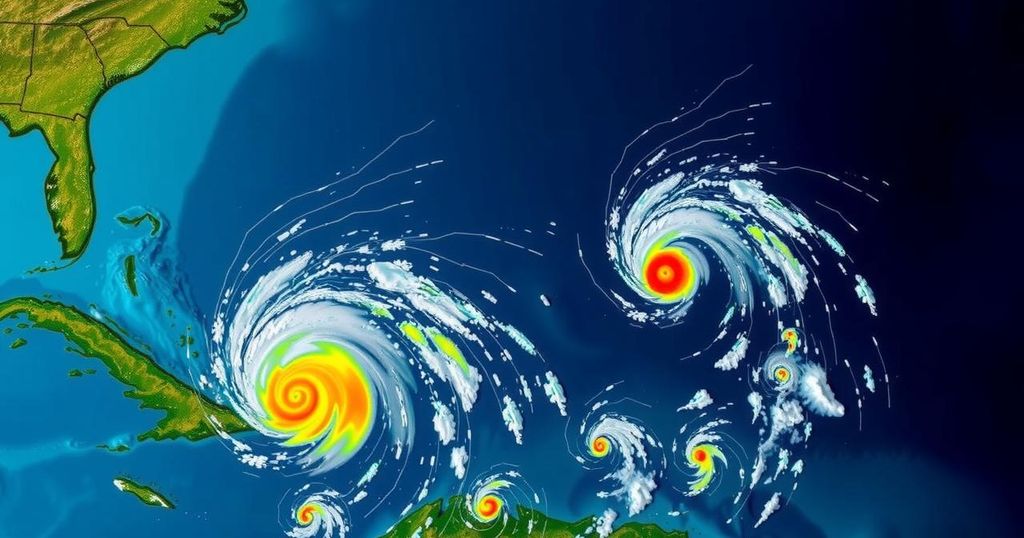
The 2024 Atlantic hurricane season witnessed 18 named storms, including 11 hurricanes and 5 major hurricanes. It began vigorously with Hurricane Beryl but experienced a mid-season lull. A resurgence occurred in late September, notably with Hurricane Helene, leading to devastating impacts. Climate change remains a critical factor in the intensity and rainfall associated with these storms, posing challenges for future preparations.
The 2024 Atlantic hurricane season concludes with a total of 18 named tropical storms, of which 11 reached hurricane status, and five were categorized as major hurricanes, classes three and above. This season included a remarkable start with Hurricane Beryl, which became the earliest category five hurricane on record. However, a subsequent lull in activity occurred throughout the middle of the season, resulting in fewer storms than anticipated, despite favorable conditions such as above-average sea surface temperatures.
Late September marked a resurgence, highlighted by Hurricane Helene, which caused significant destruction and claimed over 150 lives. Subsequent storms, including Hurricane Milton, exhibited rapid intensification, demonstrating the potential for enhanced hurricane activity. By the season’s end, Tropical Storm Sara brought substantial rainfall to Central America, underscoring the persistent risks associated with hurricane formation. Climate change has been identified as a significant factor, with studies indicating its influence on increased wind speeds and rainfall intensity during the season.
The Atlantic hurricane season typically spans from June 1 to November 30. Due to climate change, it has been observed that while the overall number of hurricanes may not increase, the storms that do form are likely to be more intense and produce more precipitation. This increased severity is attributed to rising sea temperatures, which are believed to fuel hurricane development. This year’s season illustrates these trends with mixed activity, including several powerful storms following a quieter mid-season period.
In conclusion, the 2024 Atlantic hurricane season exhibited noteworthy extremes, beginning with an unusually active start and ending with significant impacts from major hurricanes. The season confirmed the complexities of hurricane formation, influenced heavily by climate conditions. Climate change continues to play a pivotal role in shaping the attributes of storms, highlighting the need for ongoing observation and preparation for future hurricane seasons.
Original Source: www.bbc.com



Post Comment